Topologies
Topologies refer to how networks are physically set-up (how they are all connected with wires or wirelessly).
There are many topologies, many of which that are no longer used. We are going to cover 3 main ones covered by the different Computer Science specifications.
- Star
- Bus
- Mesh
Star Topology
On a star topology network all devices are connected to a central switch. A common misconception is that computer connect directly to a server, however servers connect to the switch just like every other device on the network.
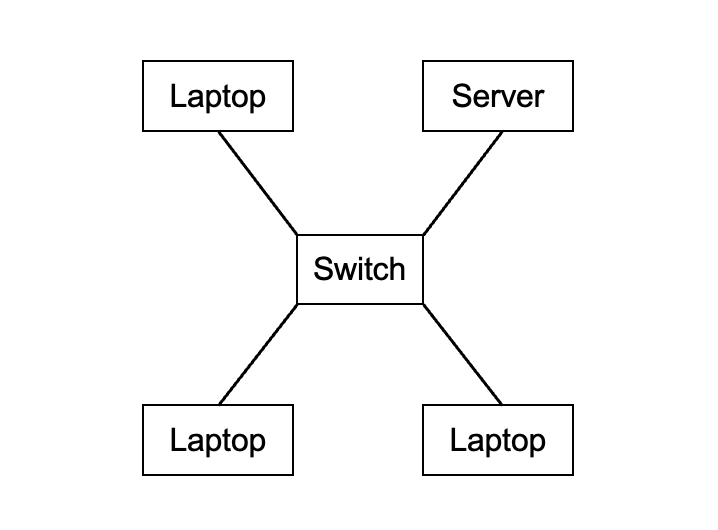
Computers can be connected via wires or wirelessly (when using a WAP).
Benefits
- If one computer fails, the rest of the network continues to function.
- Each computer has a dedicated line to the switch and doesn’t share its bandwidth with theother computer.
- Easy to add a computer to the network (new computers simply plugged into the switch using a cable)
Drawbacks
- Requires a switch, which can be expensive on larger networks
- Switch is a single point of failure (if it breaks down you don’t have a functional network).
Mesh Topology
On a mesh networks computers connect to each other without a switch, often making multiple connections to different computers.
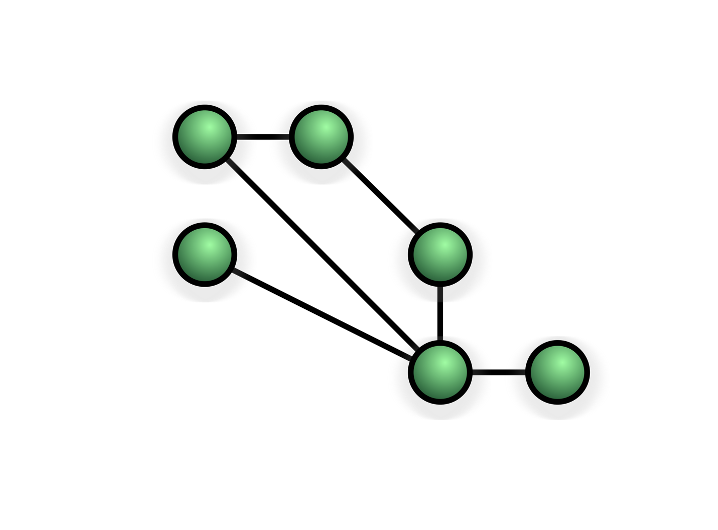
Sometimes all devices on the network will be connected to every other device (full mesh) and other times they connect through each other (partial mesh - shown above).
Benefits
- No single point of failure
- Computers failing will not impact data being sent to other computers
- Very reliable due to multiple routes to every computer
Drawbacks
- Expensive if connected with wires
- Cannot be set-up without an expert
- Difficult to maintain
Bus Topology
On a bus network all computers are connected to a single cable and at the end of the bus network cable is a terminator – this stops the signal on the cable being reflected back. This is an old topology which is no longer used – it has many disadvantages compared to modern topologies.
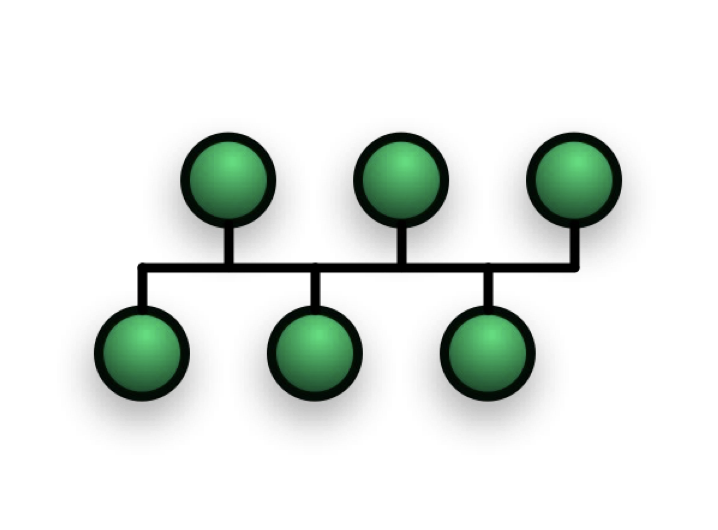
Benefits
- Easy to add a computer to the network
- Low cost – requires less cabling than a star or mesh topology network
Drawbacks
- All computers sharing the cable means that the network will not scale well with additional computers
- If there is a break in the bus network cable all of the computers will not be able to use the network
- Every computer on the network receives all data – this can be a security risk