Von Neumann Architecture
Von Neumann suggested the following architectrue, where instructions are stored in memory. On modern day computers this memory could be RAM or Secondary storage, however in this architecture refers to a memory store closer to the concept of RAM.
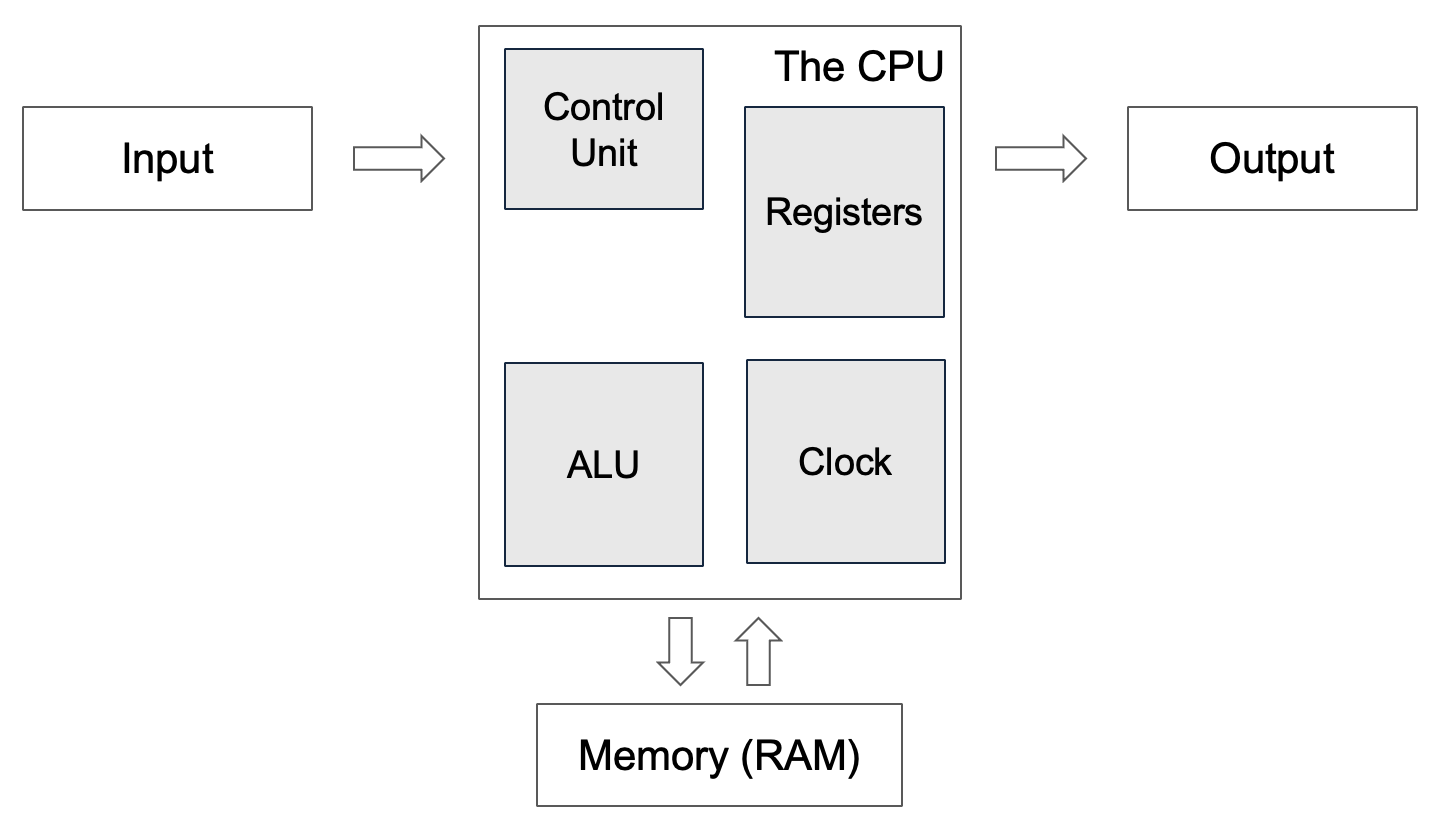
Parts described in the architecture
| Term | Definition |
| Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) | The ALU carries out two main tasks: Carries out Arithmetic (+,-,/,*) and Logic operations (AND, OR, NOT). |
| Control Unit | Controls what the CPU is doing. Sends signals to control the flow of data inside the CPU. |
| Registers | Tiny memory locations built into the CPU. They are VERY fast at moving data around and VERY expensive to make. They can only hold a tiny amount of data. |
| Memory (Not a part of the CPU but heavily linked) | Stores data and instructions. The CPU must fetch both from the memory in order to use them. Memory is much larger than cache and registers, but it is much slower to read and write data to memory. |
| Busses | Tiny wires built into the CPU. Data, instructions and signals can be passed across these between different parts of the CPU. |
| Clock | The Clock determines “how fast” the CPU is. It ticks many times each seconds – this is measured in hz (hertz). A lot of computers can complete billions of ticks every second (1 billion ticks = 1Ghz). |